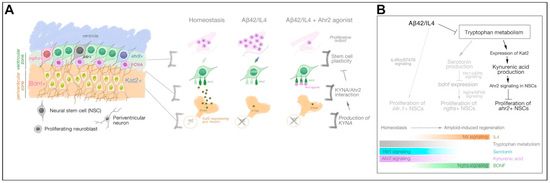
We show a new signaling mechanism through Kynurenic acid and Aryl hydrocarbon receptor in regulating the proliferation of a specific subset of neural stem cells in adult #zebrafish model of #Alzheimer‘s disease.
https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/10/10/2748